Defects of Forged Copper Valves
Defects of Forged Copper Valves
Nov 15, 2023
What is a forged copper valve?
The forged copper valve is a remarkable invention that has revolutionized the field of engineering. With its exceptional durability and versatility, this forged valve has become an indispensable component in various industries, which can be used in a wide range of applications, including plumbing systems, HVAC systems, and industrial machinery. Its ability to regulate fluid flow with precision makes it an essential component in controlling processes and maintaining system efficiency. Forged from high-quality copper, this valve exhibits exceptional strength and resistance to corrosion. Its unique composition allows it to withstand extreme temperatures and pressures, making it ideal for use in demanding environments such as oil refineries and chemical plants. Furthermore, the forging process enhances the structural integrity of the valve, ensuring its longevity and reliability. In addition to its functional benefits, the forged copper valve also offers environmental advantages. Copper is a highly sustainable material that can be recycled indefinitely without losing its properties. This makes it an eco-friendly choice for industries striving towards sustainability.
While forged copper valves offer numerous advantages like excellent conductivity and durability, they also have some notable disadvantages. These include high cost, increased weight compared to other materials, and limited resistance against certain corrosive environments. Therefore, it is crucial for industries to carefully evaluate their specific requirements before choosing forged copper valves as a suitable solution for their applications.
Firstly, one major drawback of forged copper valves is their high cost. The process of forging copper requires specialized equipment and skilled labor, which adds to the overall production expenses. Consequently, the final product becomes more expensive compared to other valve materials such as brass or stainless steel. This can pose a significant financial burden for industries operating on tight budgets. Secondly, forged copper valves are relatively heavy compared to other valve materials. This can be problematic in applications where weight is a critical factor. For instance, in aerospace or automotive industries where reducing weight is essential for fuel efficiency and performance optimization. Furthermore, although copper is known for its corrosion resistance properties, it is not entirely immune to certain corrosive environments. In highly acidic or alkaline conditions, forged copper valves may still experience some level of corrosion over time. This limits their suitability for applications requiring extreme chemical resistance.
In conclusion, the forged copper valve is a remarkable innovation that has transformed engineering practices across various industries. Its durability, versatility, and environmental benefits make it an invaluable component in modern-day systems. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further improvements in this already exceptional invention.
Defects of forged copper valves
The valve body of the copper ball valve, especially the ball valve body used for combustible gas, most valve companies will choose to use forging as much as possible in order to ensure its main pressure-bearing performance. First, forging copper valves have the advantages of improving the internal structure and the mechanical properties of the metal; second, they have high labor productivity; third, they are widely used and have weights less than one kilogram to hundreds of tons; fourth, forged copper valves can be manufactured with single pieces, small batch and mass production; fifth, precision die forging can make the size and shape of forgings close to finished parts, thus greatly saving metal materials and reducing cutting processing hours. However, the disadvantage of forging is that it cannot forge forgings with complex shapes.
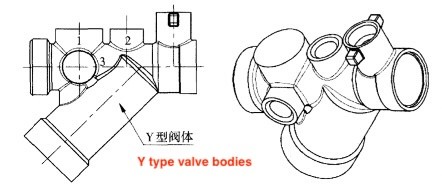
Figure 1 Ball valve bodies
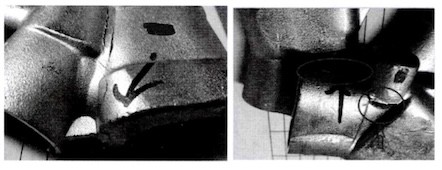
Figure 2 Locations of cracking in ball valves
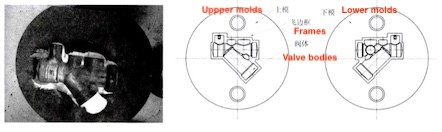
Figure 3 Closed upper and lower flat molds
Analyzing defects
Generally, valve bodies are forged using Half molds. The mold structure is mature and can forge valve bodies with relatively simple shapes and structures. The half mold is currently the most popular domestic valve body forging mold. One of the commonly used molds. However, as the environmental requirements and media for valve body assembly change, customers require that the valve be multi-functionally integrated. Figure 1 is a ball valve body. The Y-shaped part can be equipped with either a filter or a flow valve core, and the upper and down bypass hole can be equipped with a flow detection device. At the same time, to inhibit dezincification corrosion and further improve the corrosion resistance of the alloy, small amounts of arsenic or silicon are usually added to the composition to form DZR CW602N arsenic brass and lead-free Silicone brass (Table 1), but this type of brass has poor flow and a tendency to stress corrosion cracking. For example, if half core-pulling mold is used for molding, forging molding is very difficult. Unavoidable defects such as cracking at the end or internal cold insulation at transition parts often occur. The location of the defects is shown in Figure 2.
Table 1 Standard chemical compositions of arsenic brass DZR CW 602N and lead-free silicon brass
The forged copper valve is a remarkable invention that has revolutionized the field of engineering. With its exceptional durability and versatility, this forged valve has become an indispensable component in various industries, which can be used in a wide range of applications, including plumbing systems, HVAC systems, and industrial machinery. Its ability to regulate fluid flow with precision makes it an essential component in controlling processes and maintaining system efficiency. Forged from high-quality copper, this valve exhibits exceptional strength and resistance to corrosion. Its unique composition allows it to withstand extreme temperatures and pressures, making it ideal for use in demanding environments such as oil refineries and chemical plants. Furthermore, the forging process enhances the structural integrity of the valve, ensuring its longevity and reliability. In addition to its functional benefits, the forged copper valve also offers environmental advantages. Copper is a highly sustainable material that can be recycled indefinitely without losing its properties. This makes it an eco-friendly choice for industries striving towards sustainability.
While forged copper valves offer numerous advantages like excellent conductivity and durability, they also have some notable disadvantages. These include high cost, increased weight compared to other materials, and limited resistance against certain corrosive environments. Therefore, it is crucial for industries to carefully evaluate their specific requirements before choosing forged copper valves as a suitable solution for their applications.
Firstly, one major drawback of forged copper valves is their high cost. The process of forging copper requires specialized equipment and skilled labor, which adds to the overall production expenses. Consequently, the final product becomes more expensive compared to other valve materials such as brass or stainless steel. This can pose a significant financial burden for industries operating on tight budgets. Secondly, forged copper valves are relatively heavy compared to other valve materials. This can be problematic in applications where weight is a critical factor. For instance, in aerospace or automotive industries where reducing weight is essential for fuel efficiency and performance optimization. Furthermore, although copper is known for its corrosion resistance properties, it is not entirely immune to certain corrosive environments. In highly acidic or alkaline conditions, forged copper valves may still experience some level of corrosion over time. This limits their suitability for applications requiring extreme chemical resistance.
In conclusion, the forged copper valve is a remarkable innovation that has transformed engineering practices across various industries. Its durability, versatility, and environmental benefits make it an invaluable component in modern-day systems. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further improvements in this already exceptional invention.
Defects of forged copper valves
The valve body of the copper ball valve, especially the ball valve body used for combustible gas, most valve companies will choose to use forging as much as possible in order to ensure its main pressure-bearing performance. First, forging copper valves have the advantages of improving the internal structure and the mechanical properties of the metal; second, they have high labor productivity; third, they are widely used and have weights less than one kilogram to hundreds of tons; fourth, forged copper valves can be manufactured with single pieces, small batch and mass production; fifth, precision die forging can make the size and shape of forgings close to finished parts, thus greatly saving metal materials and reducing cutting processing hours. However, the disadvantage of forging is that it cannot forge forgings with complex shapes.

Figure 1 Ball valve bodies

Figure 2 Locations of cracking in ball valves

Figure 3 Closed upper and lower flat molds
Analyzing defects
Generally, valve bodies are forged using Half molds. The mold structure is mature and can forge valve bodies with relatively simple shapes and structures. The half mold is currently the most popular domestic valve body forging mold. One of the commonly used molds. However, as the environmental requirements and media for valve body assembly change, customers require that the valve be multi-functionally integrated. Figure 1 is a ball valve body. The Y-shaped part can be equipped with either a filter or a flow valve core, and the upper and down bypass hole can be equipped with a flow detection device. At the same time, to inhibit dezincification corrosion and further improve the corrosion resistance of the alloy, small amounts of arsenic or silicon are usually added to the composition to form DZR CW602N arsenic brass and lead-free Silicone brass (Table 1), but this type of brass has poor flow and a tendency to stress corrosion cracking. For example, if half core-pulling mold is used for molding, forging molding is very difficult. Unavoidable defects such as cracking at the end or internal cold insulation at transition parts often occur. The location of the defects is shown in Figure 2.
Table 1 Standard chemical compositions of arsenic brass DZR CW 602N and lead-free silicon brass
| Materials | Code | Cu | Pb | Fe | Ni | Al | Mn | Sn | As | Si | P | Zn |
| Arsenical brass | DZR CW602N | 61 to 63 | 1.7 to 2.8 | Less than and equal to 0.1 | Less than and equal to 0.3 | Less than and equal to 0.05 | Less than and equal to 0.1 | Less than and equal to 0.1 | 0.1 to 0.15 | / | / | The rest |
| Lead-free silicon | / | 70 to 75 | Less than and equal to 0.15 | Less than and equal to 0.25 | / | / | / | 0.3 to 1 | / | 2.5 to 3 | Less than and equal to 0.1 | The rest |
Next: The Improvement Plan for Forged Copper Valves
Previous: Forging Hollow Valve Spheres
News
About Us
Best Categories
Useful Links